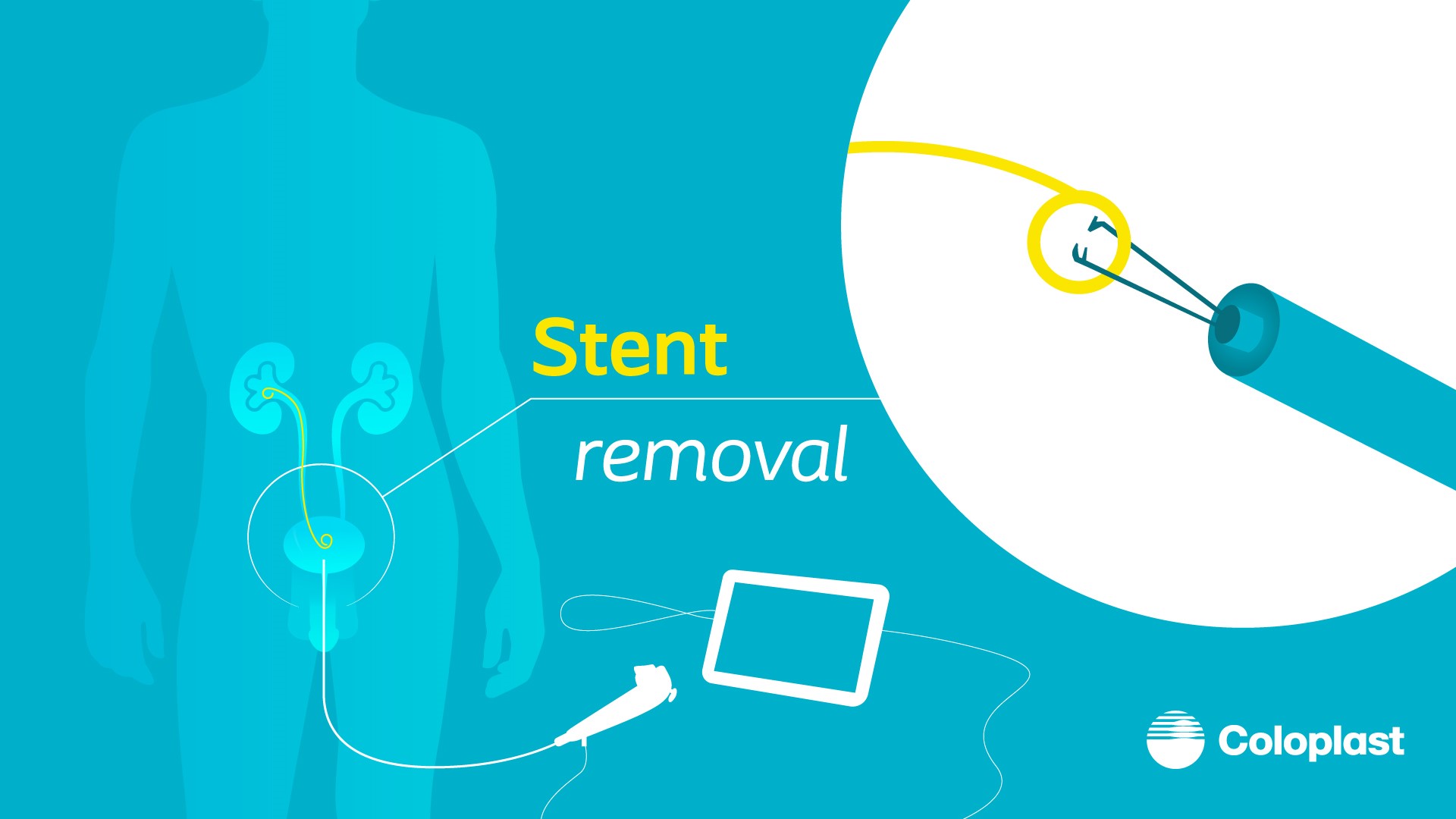
Challenges around Double-J stent removal
Ureteric stents are commonly inserted for blockages of the ureter from stones, or from external compression due to tumors. They are also left in temporarily prior to shock wave lithotripsy (SWL) or following ureteroscopy (URS) and stone treatment procedures. While stents allow these stone treatments to be carried out safely, they also have associated side-effects while they are in place.
Symptoms and their severity are unpredictable and vary among individuals. These range from increased urinary frequency, urgency to void, bladder or urethral pain, haematuria, occasional incontinence and associated referred pain in the groin, loin or genitals during or after passing urine. While the stent is in place there is also an increased risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs).
The stent side-effects affect all aspect of patient’s quality of life including physical activity, work, sexual activity, travel, social life and holidays. If left for longer than intended, they also cause stent encrustations which lead to worsening urinary symptoms, UTIs, obstruction and complications related to encrusted stent requiring additional procedures to remove it.

Although stents are commonly used at the urologist’s preference and as a safety net for clinical cases, the dwell time should be kept to a minimum to reduce stent side-effects and related complications. The stent removal should be expedited and ideally be done in the outpatient clinic. One such device which can help to remove the stent is the Isiris® α single-use dedicated flexible cystoscope with an in-built stent removal grasper. It allows for prompt removal of the ureteral stent without a dedicated assistant.
According to our experience*, Isiris α significantly reduces stent dwell time from 27 to 15 days, procedural time from 14 to 2 minutes, staffing and cost associated with it. On one hand, it allows the stent removal to be done in an outpatient setting. This allows avoiding agenda pressure of the operating theatre or endoscopy room on stent removals, thus managing short dwell times as expected. On the other hand, this also indirectly reduces the organizational pressure in operating theatre and endoscopy rooms and decreases the cost of the procedure. As a single use scope, there is no cost related to re-processing of a reusable scope or graspers, and no cross-infection risk. This is especially useful in patients with renal transplant who need stent removal after their transplant surgery.
As a result of using the Isiris α system, more endoscopy slots and operating theatre slots can be created which can help deal with other diagnostic and therapeutic urological procedures. This gives us more capacity for the diagnostic cystoscopy time which is needed for cancer diagnostics and follow-up. Knowing that prolonged dwell times may be associated with more UTIs and encrustation risk, and that early stent removal leads to fewer emergency and hospital admissions, the capability of Isiris α scope system to allow shorter dwell times is very welcome.
Stent removal is usually done as an isolated procedure when performed using a reusable scope as it requires a camera-stack system. In our experience with use of Isiris α in an outpatient clinic setting, there is no need for this set-up, and the immediate post-operative follow-up can also be done at the same session, thereby saving time and cost to both the patient and the organization.
The clinical experience of using Isiris α has also been rated favourably with an overall satisfaction as ‘good or very good’ by 90-92% of urologists*. Isiris α stent removal system was shown in our unit to have multitude of benefits, and previous scientific evidence confirms these findings. These relate to patient benefits by reducing stent dwell time, which is expected to increase their quality of life, reduce their visits to the hospital for side-effects or complications, and having the follow-up at the same time as their stent removal is convenient*. The hospital and organizational benefits relate to better use of resources such as operating theatre and endoscopy rooms, which decreases the waiting times of other diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, reduces cost of stent removal and readmissions from complications related to prolonged stent dwell time.
Although stent usage should be minimised, the use of Isiris α seems to be helpful in patients who have a stent inserted, and this would be beneficial to surgeons and patients alike.
*Pietropaolo A, Hughes T, Tear L, Somani BK. Comparison of ureteric stent removal procedures using reusable and single-use flexible cystoscopes following ureteroscopy and lasertripsy: A micro costing analysis. Cent European J Urol. 2020; doi: 10.5173/ceju.2020.0159
Isiris® α is a sterile, single-use flexible cystoscope designed for removal of double loop ureteral stents accessible in the bladder via urethral insertion in adults. Isiris® α has been designed to be used with the reusable Isiris® Monitor to visualize the observations obtained by Isiris® α.
Warnings
- Do not use active endoscopic accessories such as laser probes and electrosurgical equipment in conjunction with the Isiris® System, as this may result in patient injury or damage to the Isiris® System.
- Do not use the Isiris® System if it is damaged in any way.
- Isiris® α is a single-use device. Isiris® α is considered infected after use and must be disposed of in accordance with local guidelines for the collection of infected medical devices with electronic components.
- Do not soak, rinse, or sterilize this device as these procedures may leave harmful residues or cause malfunction of the device. The design and material used are not compatible with conventional cleaning and sterilization procedures.
- The Isiris® System is neither MRI safe nor MRI compatible.
- Excessive force should never be used when operating Isiris® α.

- Happy Valentine’s from Andy Barham, Patient Educator
- Why should you always have an Elefant in the room? Discover the new Coloplast website
- The first and only 522 study to compare a single incision sling to full-length retropubic and transobturator slings
- Healing architecture,“Making space for the human touch”
-
Learn more about our Women’s Health portfolio and the experiences of your colleagues in the Netherlands and Belgium
Virtually, February 3 2022 -
115th Congress of the AFU 2021
Havane Bordeau, November 17 2021 -
Online Kiel School of Penile Surgery Registration is OPEN FROM NOW
Virtually, November 29 2021